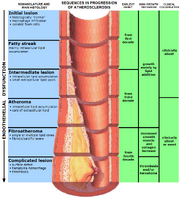
Atherosclerosis is a disease affecting arterial blood vessels. It is a chronic inflammatory response in the walls of arteries, in large part due to the accumulation of macrophage white blood cells and promoted by low density (especially small particle) lipoproteins (plasma proteins that carry cholesterol and triglycerides) without adequate removal of fats and cholesterol from the macrophages by functional high density lipoproteins (HDL), (see apoA-1 Milano). It is commonly referred to as a "hardening" or "furring" of the arteries. It is caused by the formation of multiple plaques within the arteries.
When it affects the coronary artery, it is referred to as coronary artery disease. It is the most common type of heart disease. A generalized restriction of blood flow to the heart is referred to as ischemic vascular disease (IVD).