Assyria was a Mesopotamian empire that existed from 2500 BC to 609 BC, with Assur and Nineveh serving as its capitals. The city of Assur was established in 2600 BC, and Assyria was later conquered by the Akkadian Empire. Assyria later rebelled against Sargon the Great, who massacred the Assyrians during their uprising. In 2154 BC, the Akkadian Empire was destroyed by the Gutians, and Assyria once again became independent.
From 2025 BC to 1750 BC, the Old Assyrian Empire was in power, and it conquered several city-states in Mesopotamia. From 1450 BC to 1393 BC, Assyria declined due to outside invasions, and Assyria became too weak to fight against either the Hittites or the Mitanni Empire. From 1392 BC to 934 BC, the Middle Assyrian Empire was in existence, eclipsing the other regional powers. The Assyrians waged several wars against the Arameans and other local nations, and Assyria became a warrior society; all free male citizens were obligated to serve in the army for a time. Assyria remained the most powerful nation even during the Bronze Age collapse.
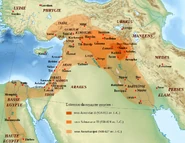
In 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire came to power, and Adad-nirari II cleared the Arameans from Assyria's borders and expanded into Anatolia, Iran, the Levant, and Babylonia. Ashurnasirpal II (r. 883-859 BC) subjugated much of the Levant to the west and the Medes and the Persians to the east, and he also moved the capital to Nimrud. Shalmaneser III (r. 859-824 BC) conquered to the Caucasus foothills, Israel, and Aram Damascus, also subjugating Persia and the Arabs who dwelt to the south of Mesopotamia, and driving the Egyptians from Canaan. Under Adad-nirari III (r. 811-783 BC), the Assyrians subjugated the Arameans, Phoenicians, Philistines, Israelites, Hittites, Edomites, Persians, Medes, and Manneans, penetrating as far as the Caspian Sea.
Tiglath-Pileser III (r. 745-727 BC) created the world's first professional army and conquered the Greeks of Cyprus, the Phoenicians, Judah, Philistia, Samarra, and the whole of Aramea. He then deposed the king of Babylonia and usurped the throne for himself, implementing wide-reaching reforms. Sargon II's conquest of Samaria ended the United Kingdom of Israel, and he also repelled the Scythians and Cimmerians from Persia and Media, conquered the Hittites of northern Syria and Cilicia, and founding Dur Sharrukin as Assyria's new capital. Esarhaddon launched an invasion of Egypt in 671 BC, crossing the Sinai and taking Egypt with surprising ease and speed; he destroyed the Kushite Empire in the process.
Following the death of Ashurbanipal in 627 BC, Assyria devolved into a series of civil wars, and the Scythians and Cimmerians proceeded to invade and plunder Assyrian colonies. In 614 BC, the Medes invaded Assyria, and the Medes and Babylonians allied to attack Nineveh in 612 BC. The invaders destroyed the great city of Nineveh and the Assyrian Empire, replacing it by the Neo-Babylonian Empire.